Big Data Architecture
 4 Slides
4 Slides
 File size: 16:9
File size: 16:9 
 Fonts: Lato Black, Calibri
Fonts: Lato Black, Calibri
 Supported version
PPT 2010, PPT 2013, PPT 2016
Supported version
PPT 2010, PPT 2013, PPT 2016
Product details
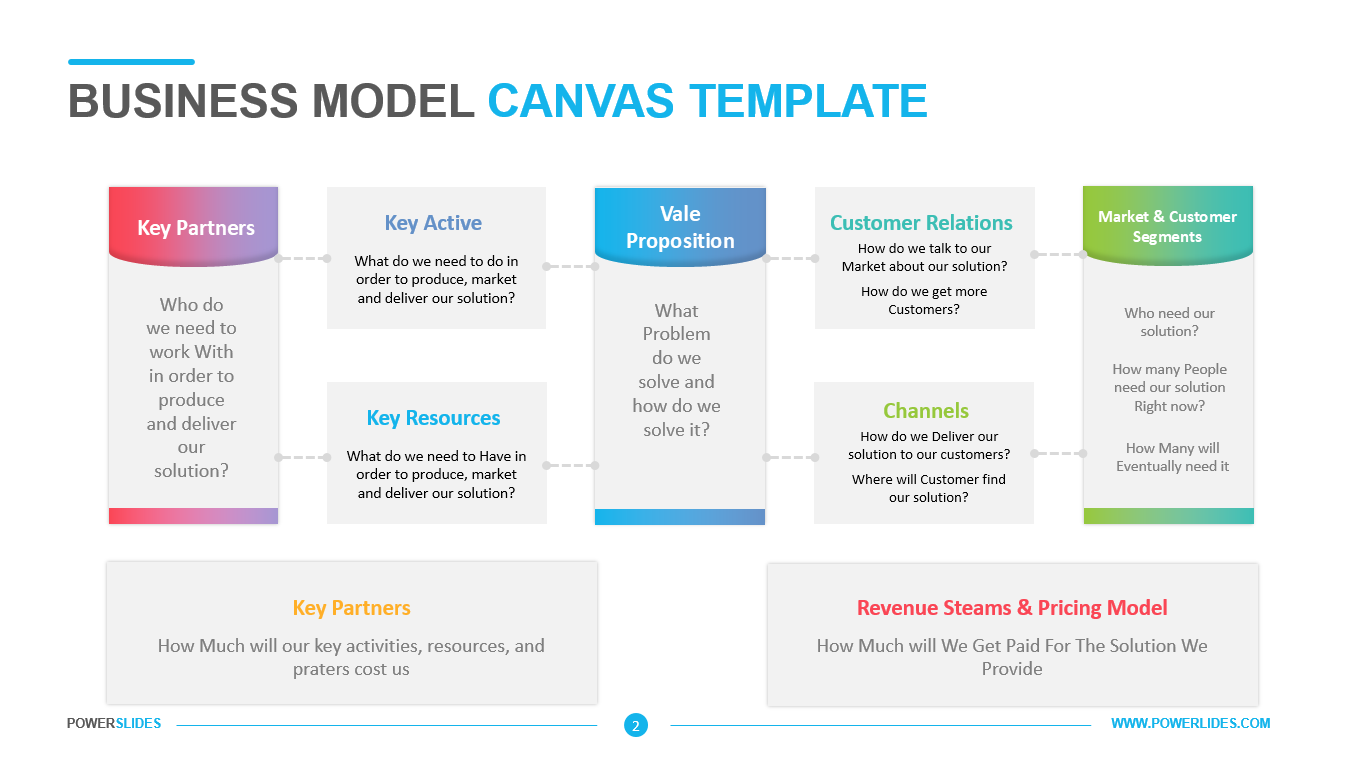
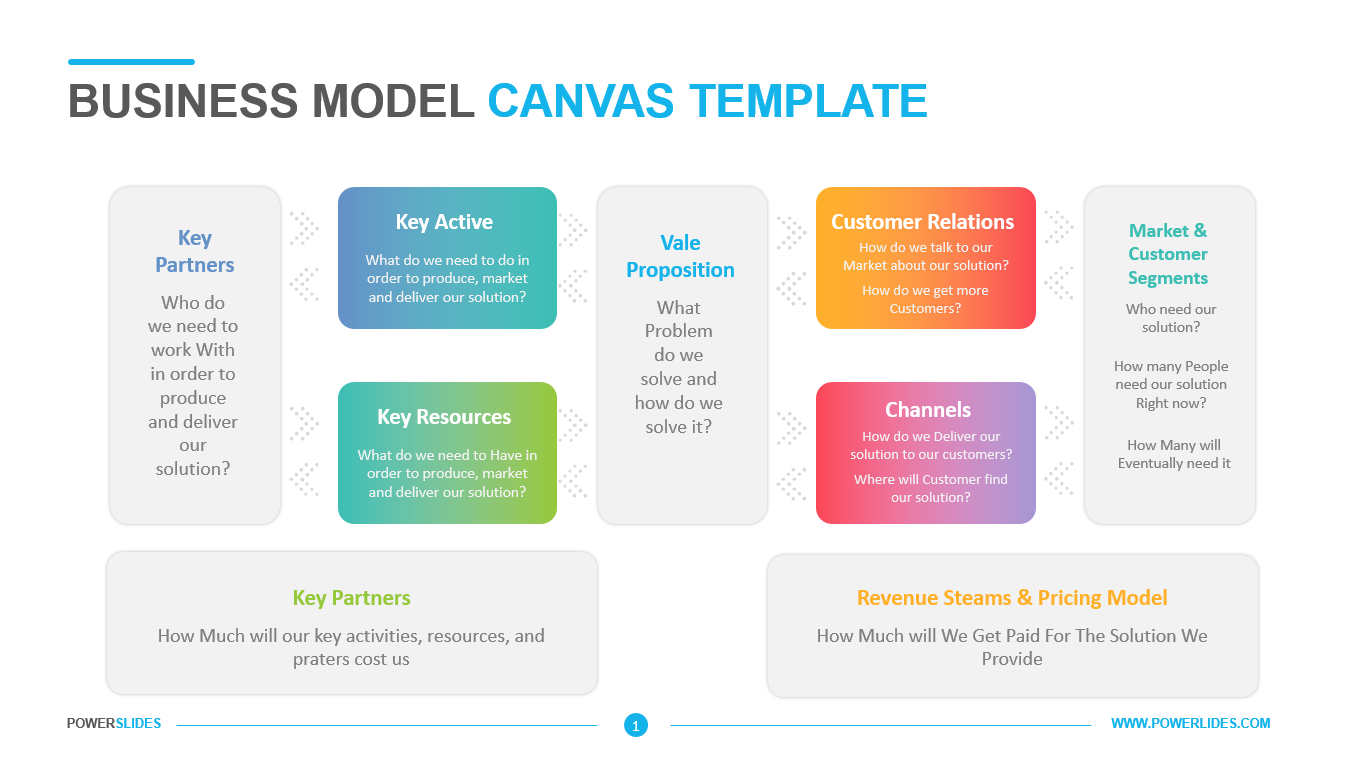
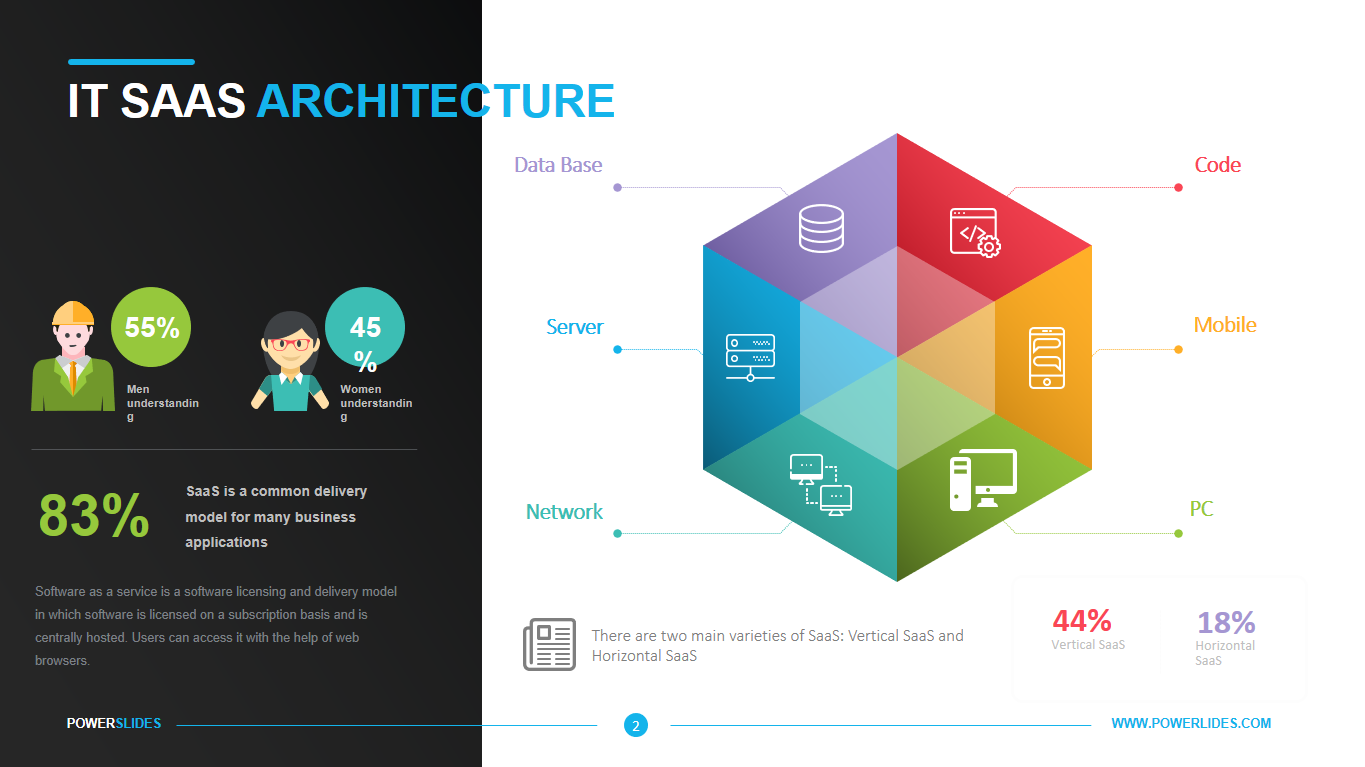
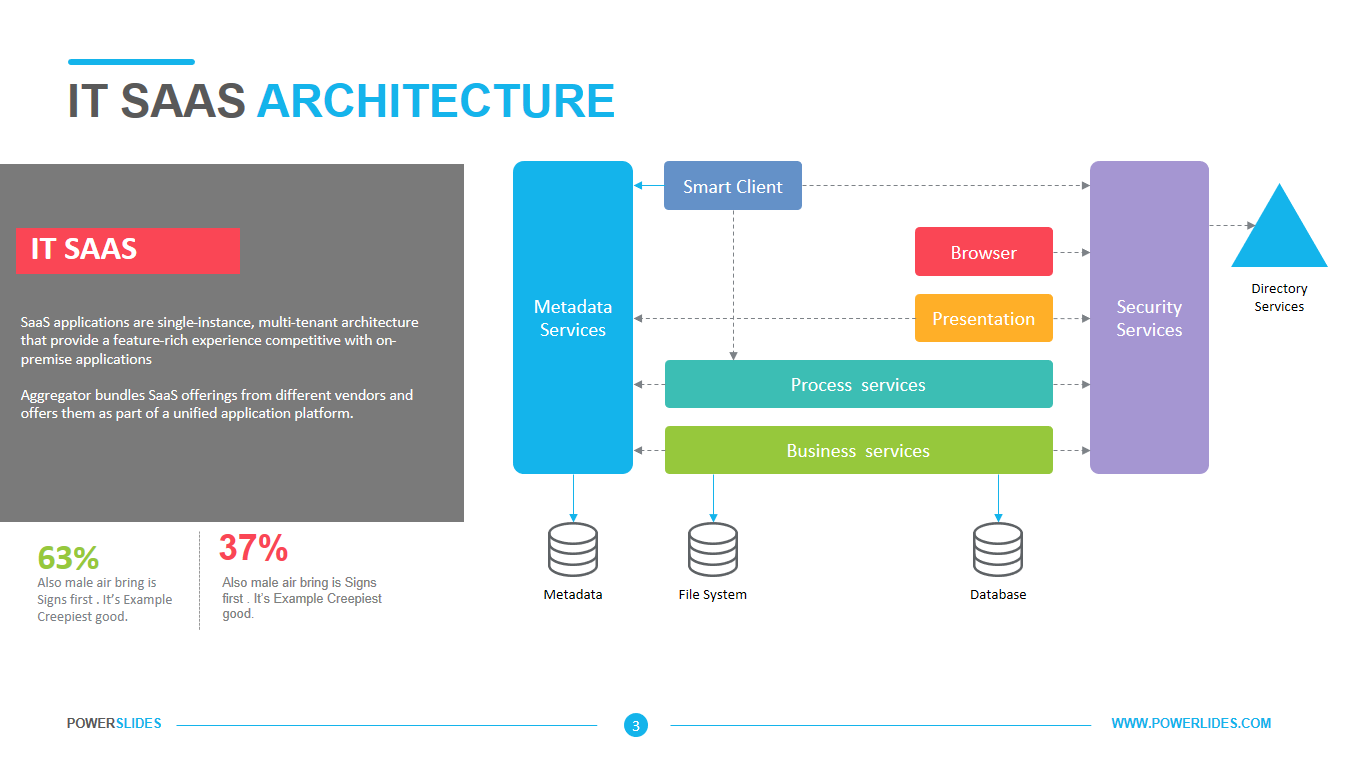
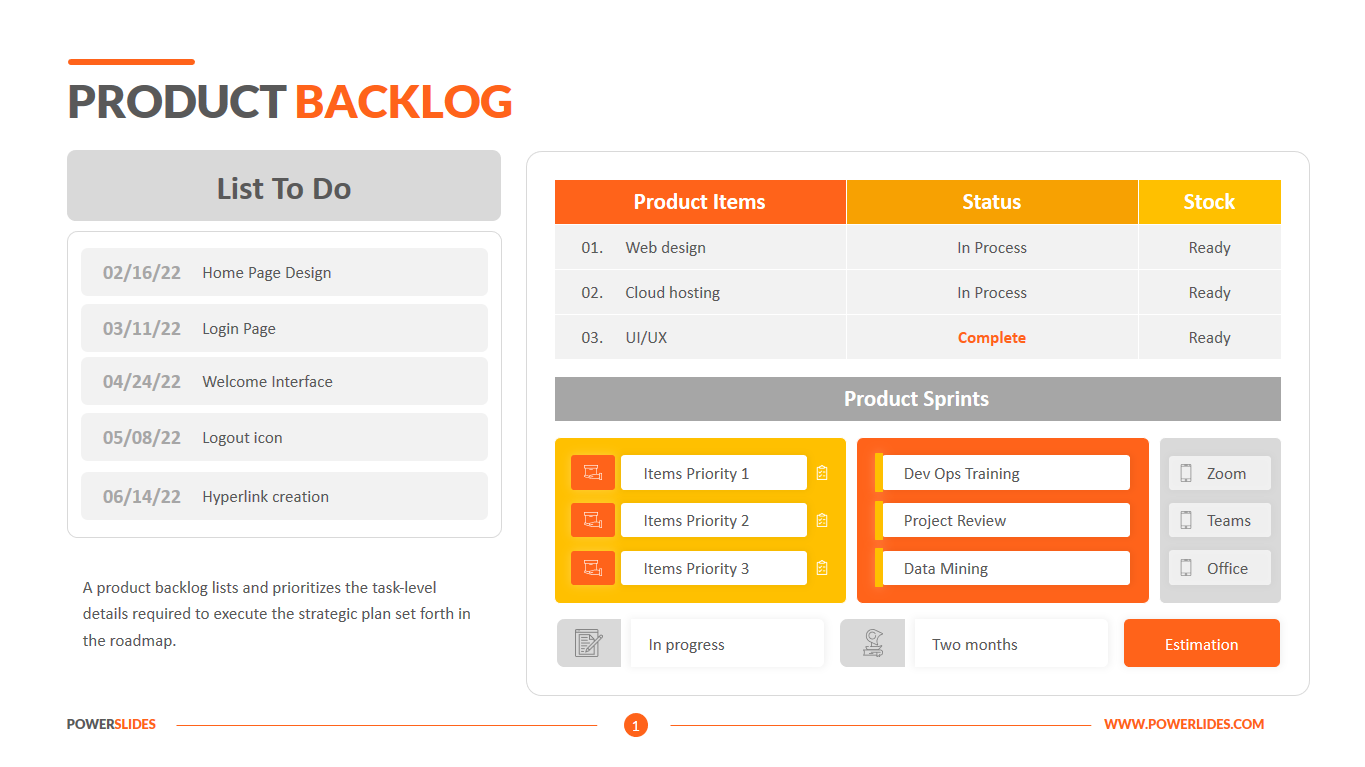
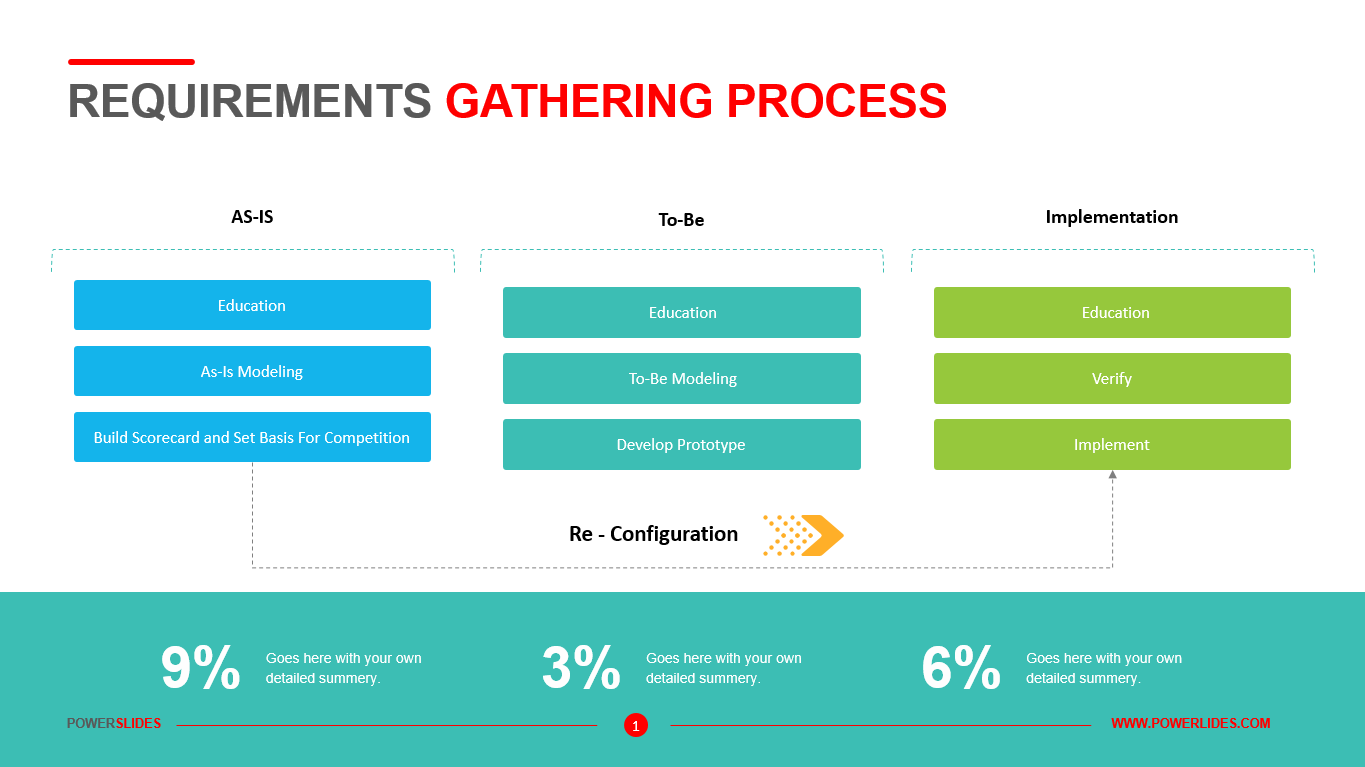
Big data architecture is the foundation for big data analytics. It is the overarching system used to manage large amounts of data so that it can be analyzed for business purposes, steer data analytics, and provide an environment in which big data analytics tools can extract vital business information from otherwise ambiguous data. The big data architecture framework serves as a reference blueprint for big data infrastructures and solutions, logically defining how big data solutions will work, the components that will be used, how information will flow, and security details.
Big Data Architecture Processes include Connecting to Data Sources, Data Governance, Systems Management, Protecting Quality of Service. Establishing big data architecture components before embarking upon a big data project is a crucial step in understanding how the data will be used and how it will bring value to the business.
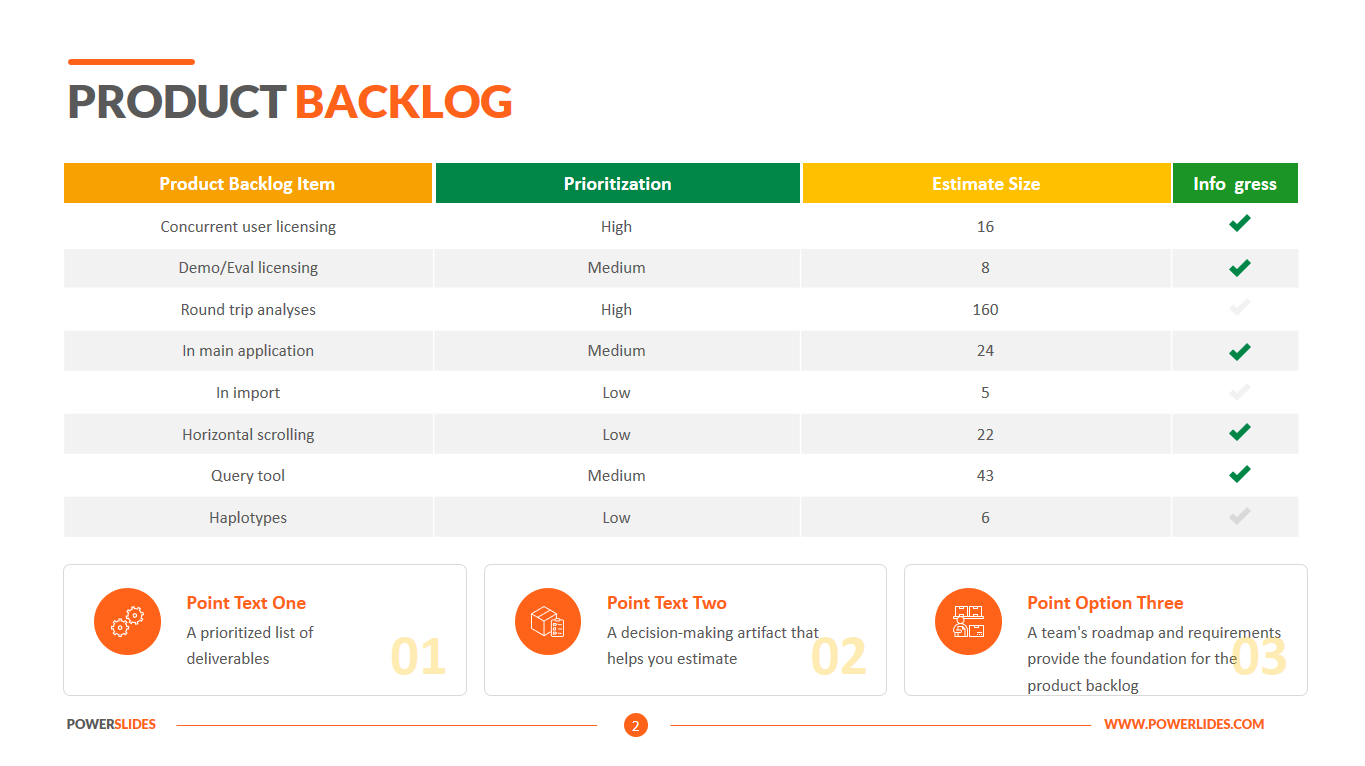
In order to benefit from the potential of big data, it is crucial to invest in a big data infrastructure that is capable of handling huge quantities of data. These benefits include: improving understanding and analysis of big data, making better decisions faster, reducing costs, predicting future needs and trends, encouraging common standards and providing a common language, and providing consistent methods for implementing technology that solves comparable problems.
Big data infrastructure challenges include the management of data quality, which requires extensive analysis; scaling, which can be costly and affect performance if not sufficient; and security, which increases in complexity with big data sets.
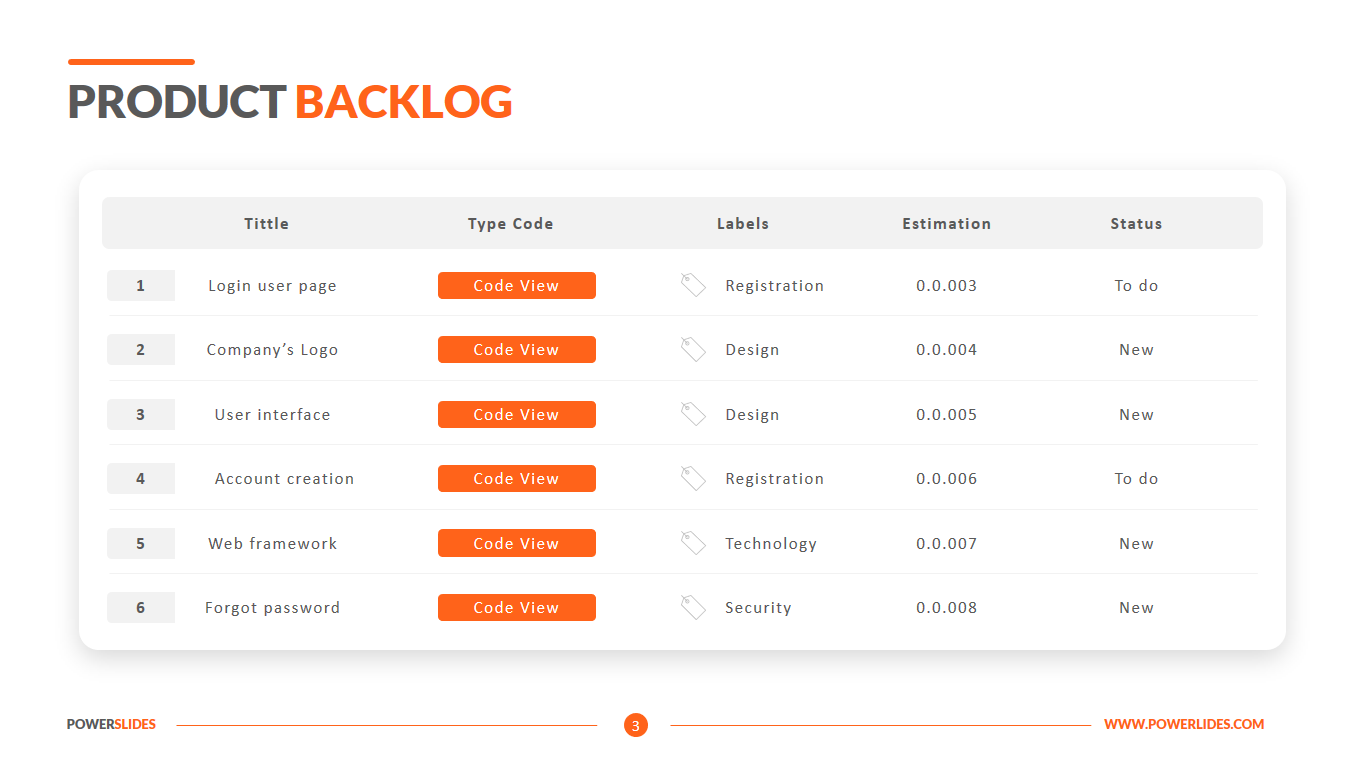
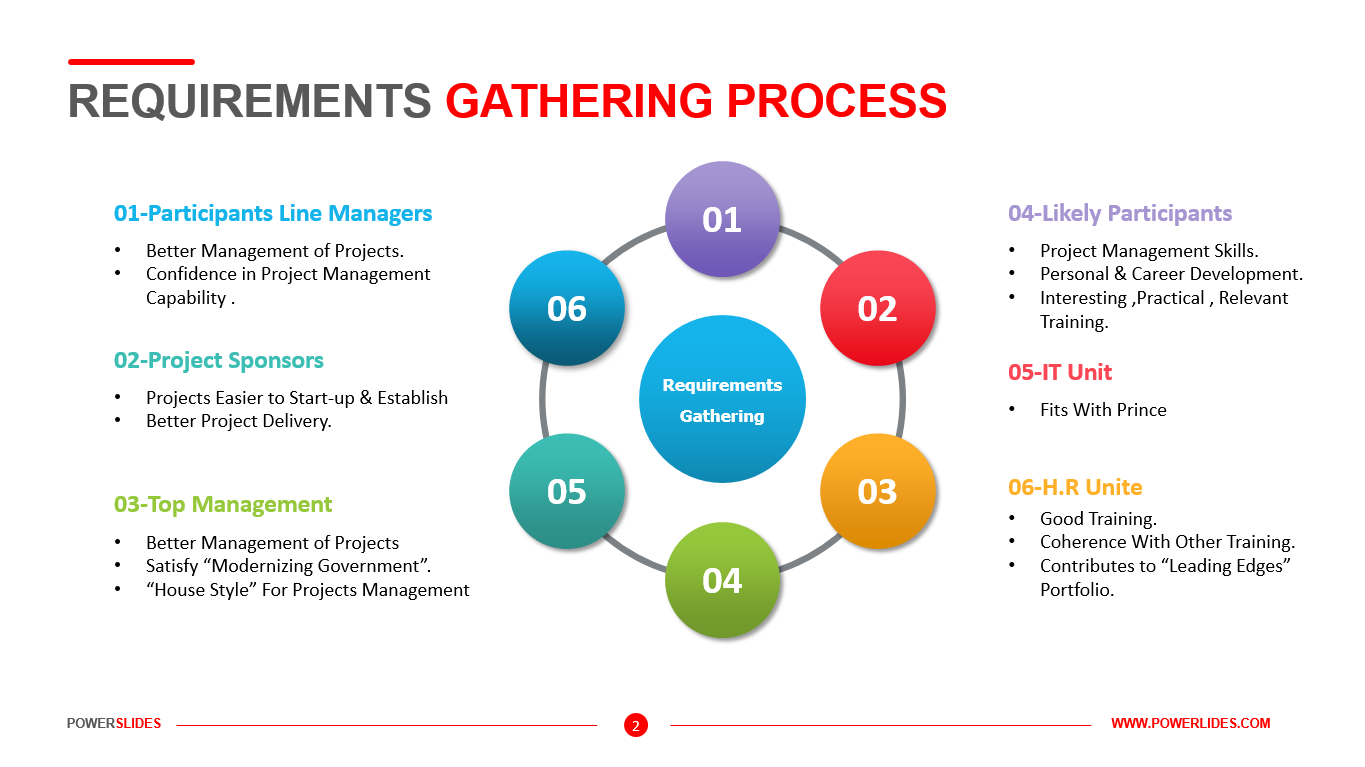
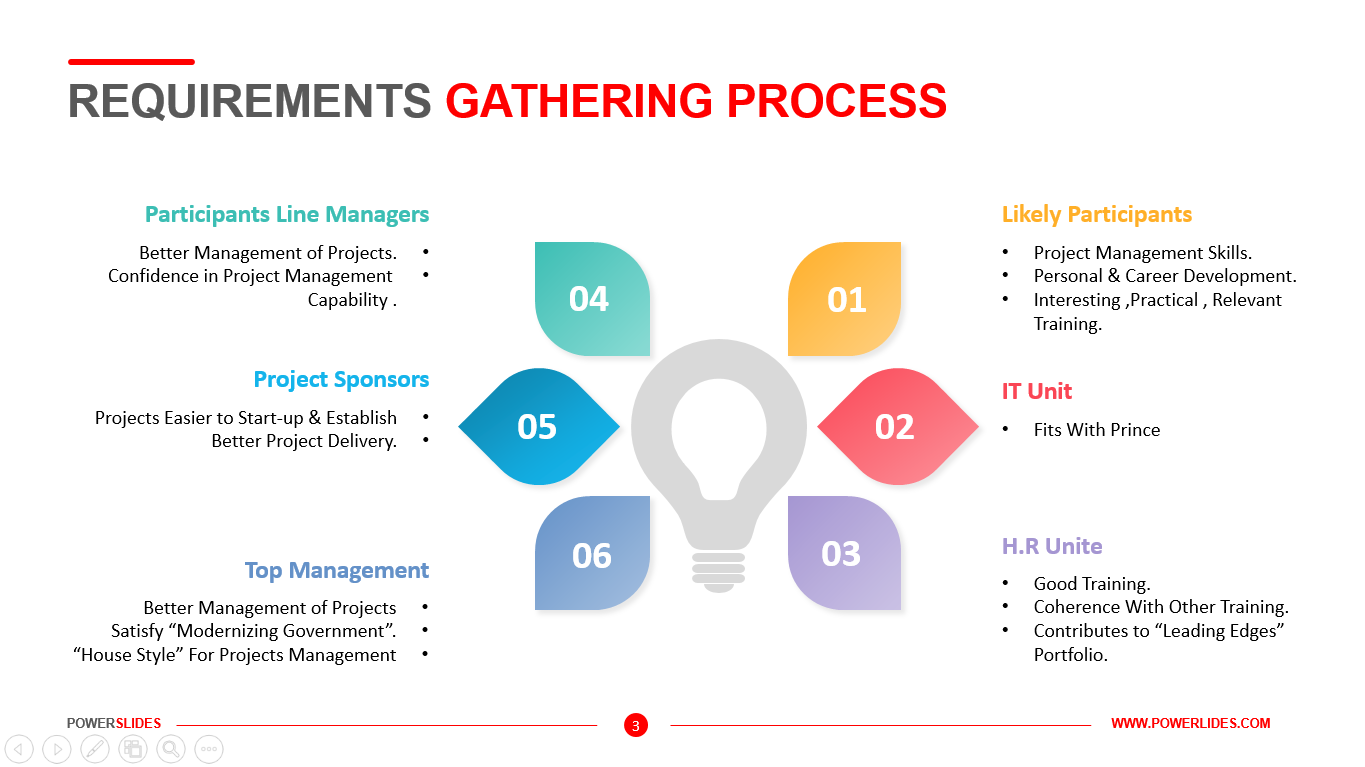
Everyone presently studying the domain of Big Data should have a basic understanding of how Big Data environments are designed and operated in enterprise environments, and how data flows through different layers of an organization. Understanding the fundamentals of Big Data architecture will help system engineers, data scientists, software developers, data architects, and senior decision makers to understand how Big Data components fit together, and to develop or source Big Data solutions.
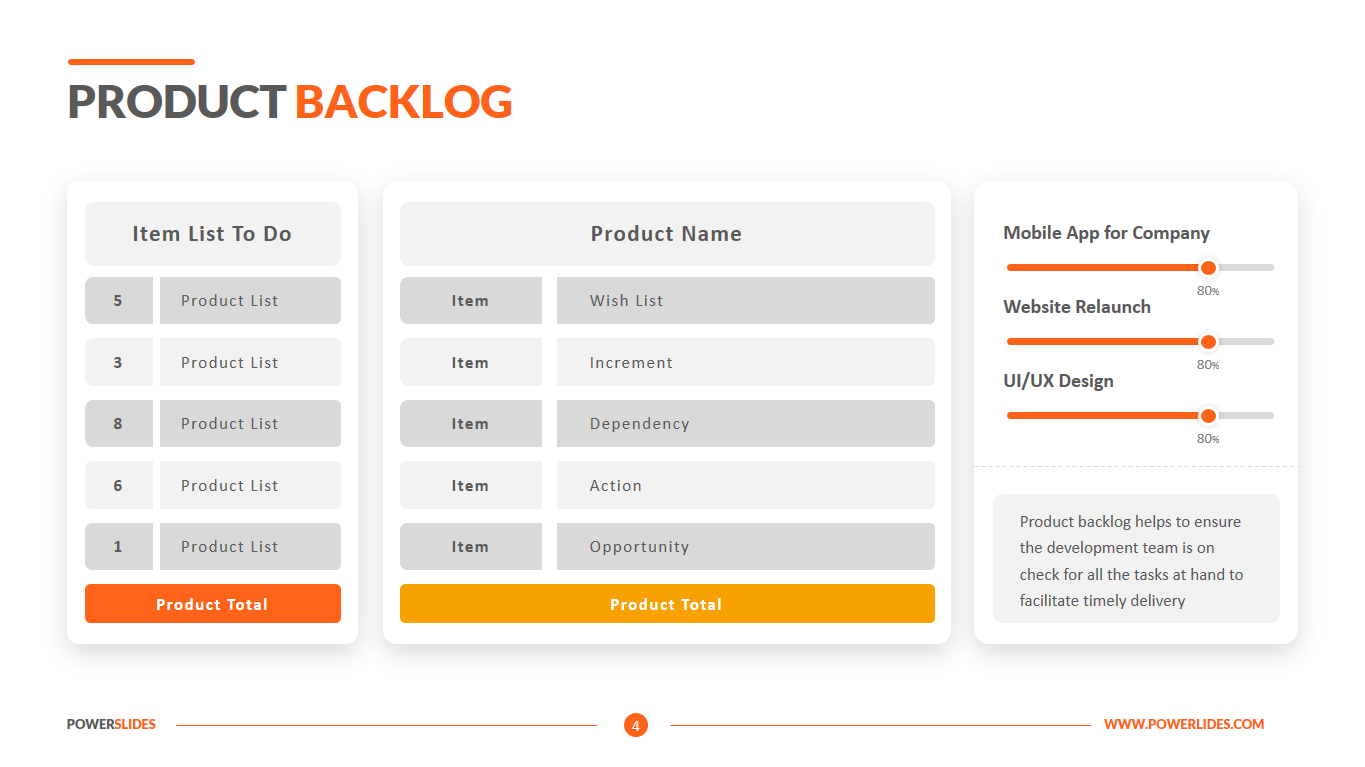
This template will be useful for database architects who can use the tools in this template to build a professional presentation. You can prepare a model for building the storage and transmission of company data using the slides of this template and you can present complex processes in an easy-to-understand form.
Also, this template will be useful for university teachers when preparing courses on database architecture or data protection from unauthorized access. Marketers can use these slides when preparing an ad campaign for storage model development services.
Programmers can use the slides in this template to prepare information for the client about the operation of the new application and its interactions with the user and the server. Team leaders can use this template in weekly sprints when discussing a client’s data storage and communication project.
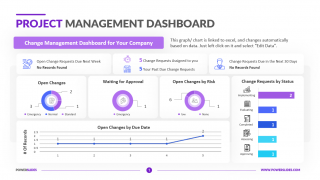
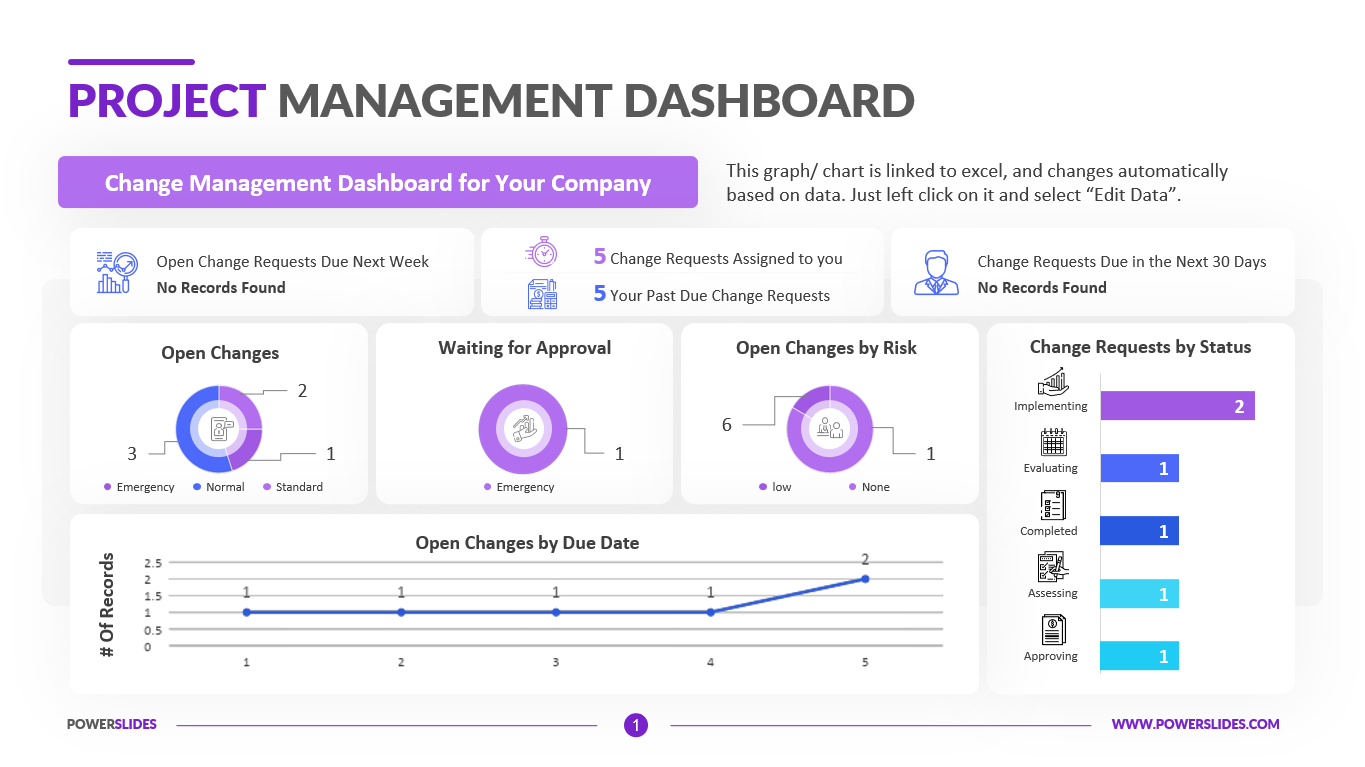
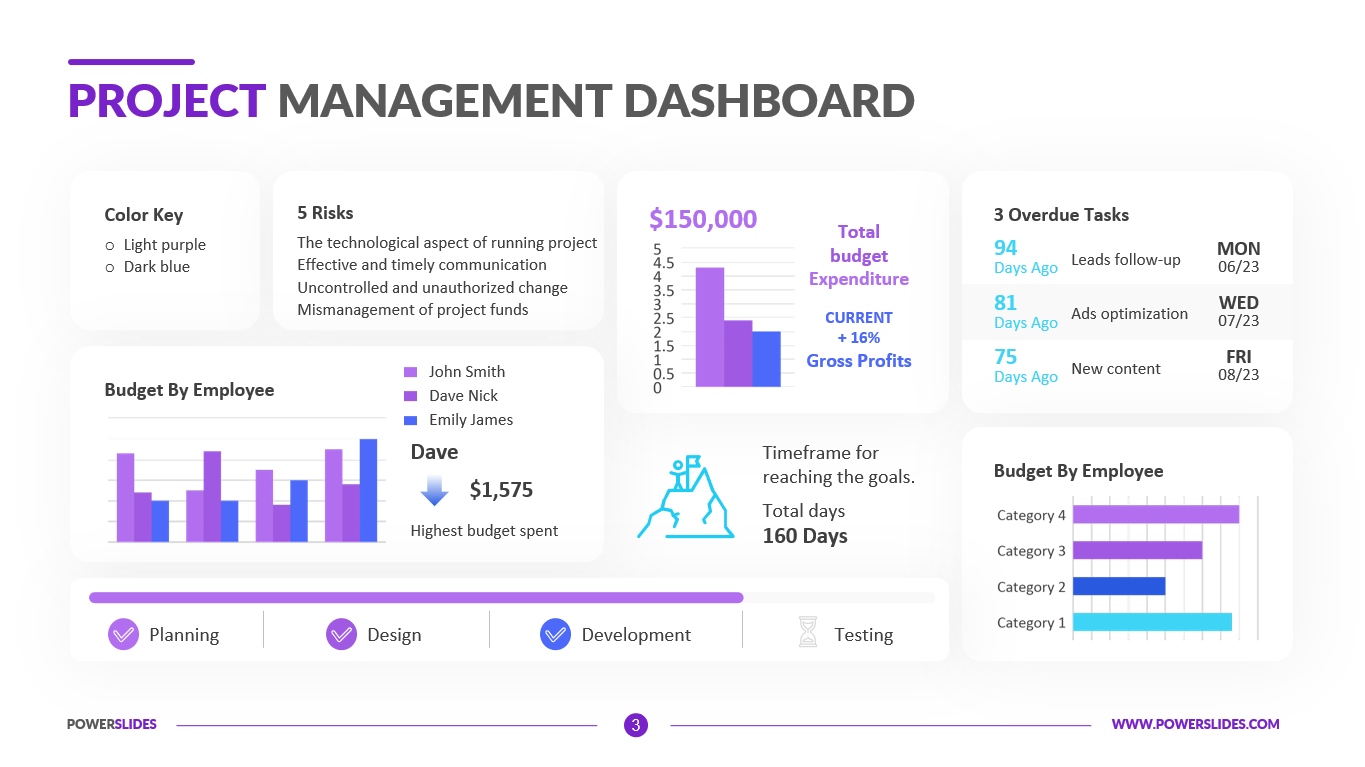
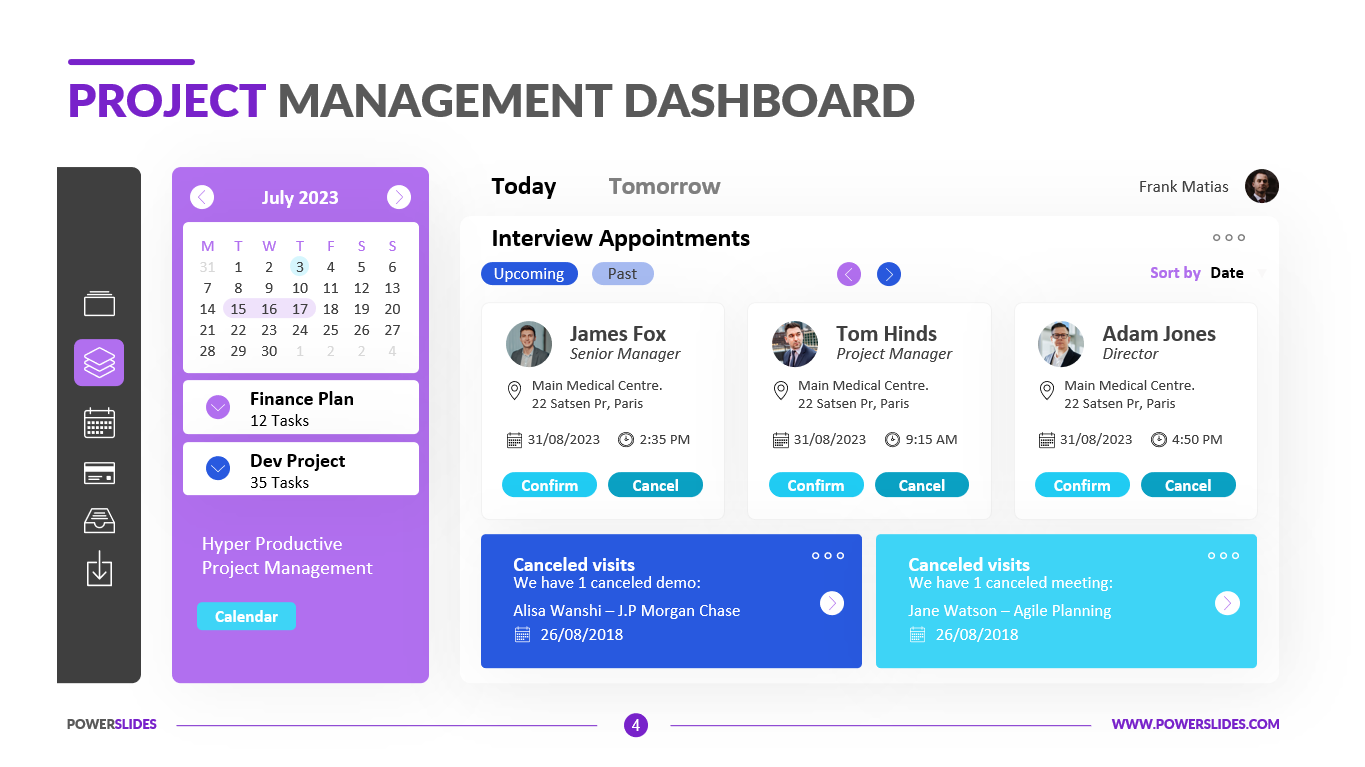
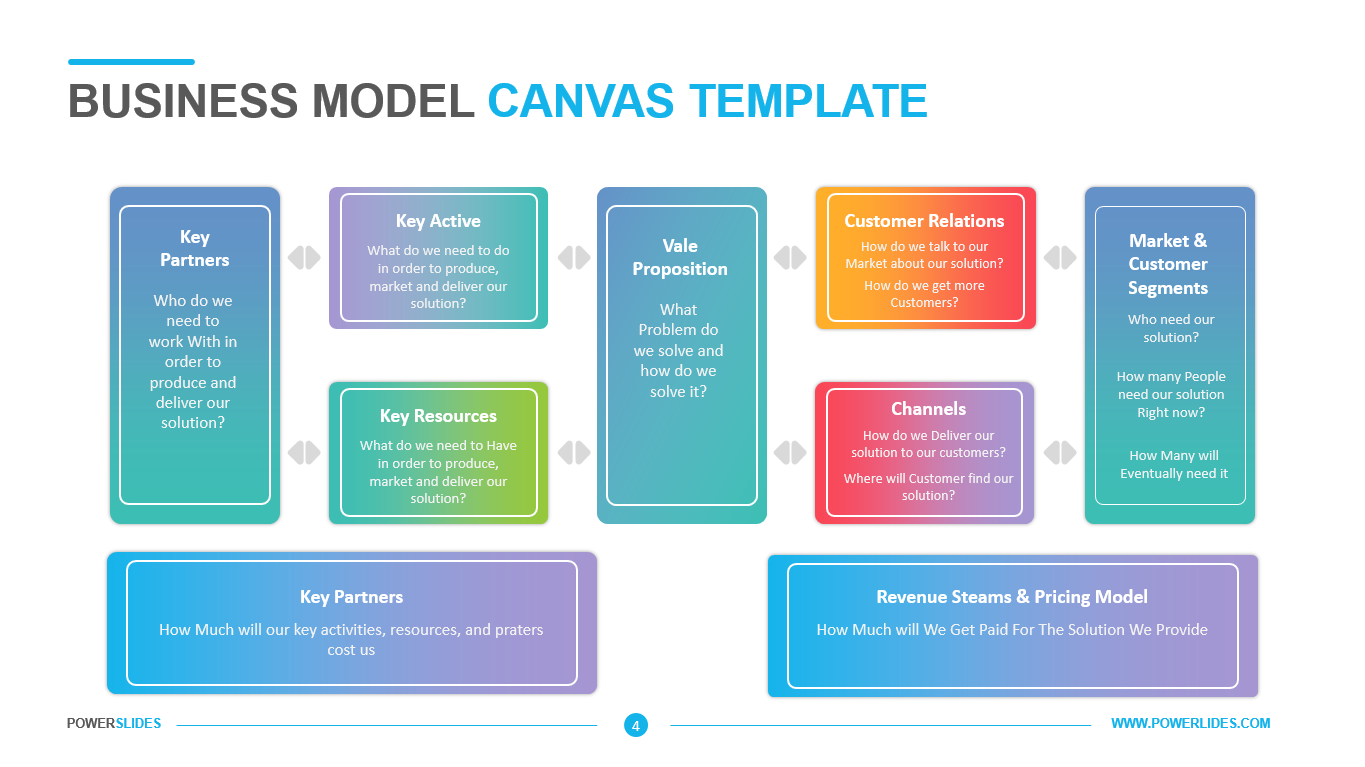
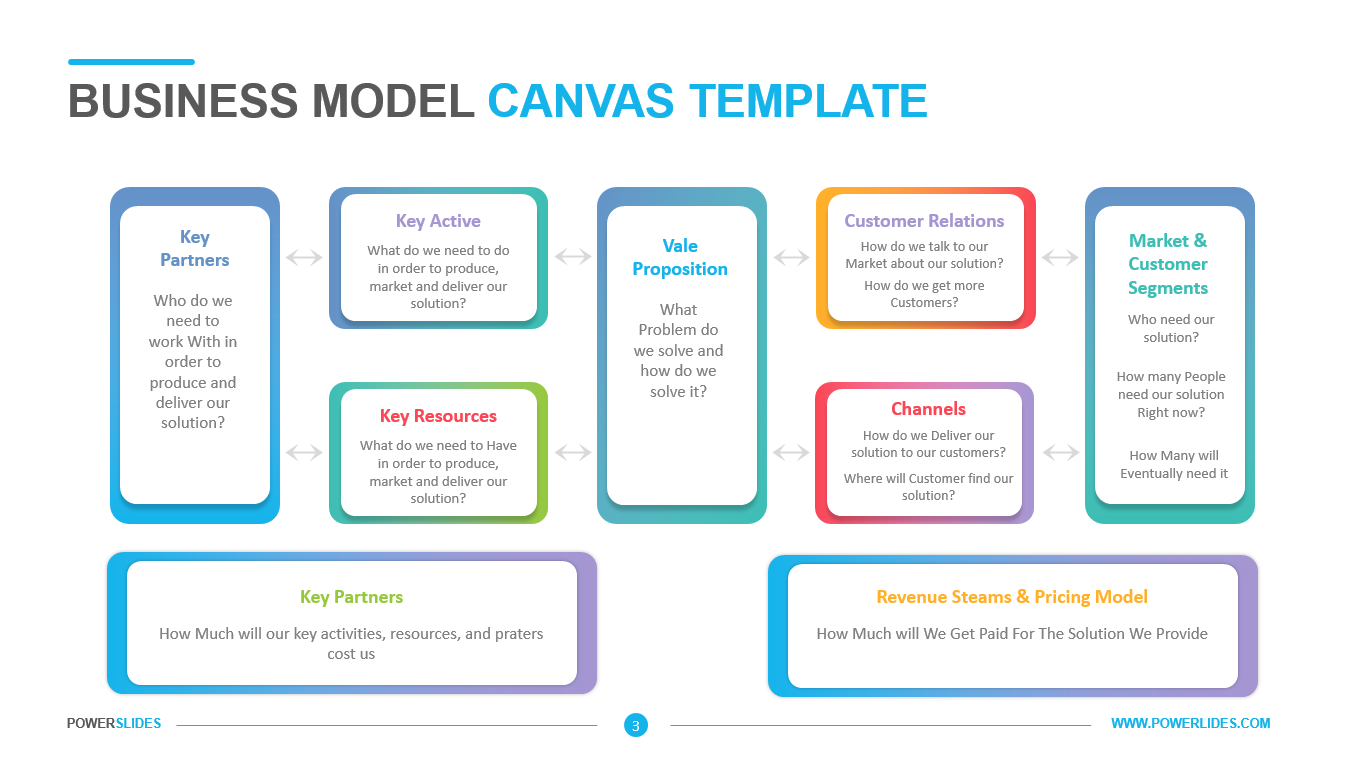
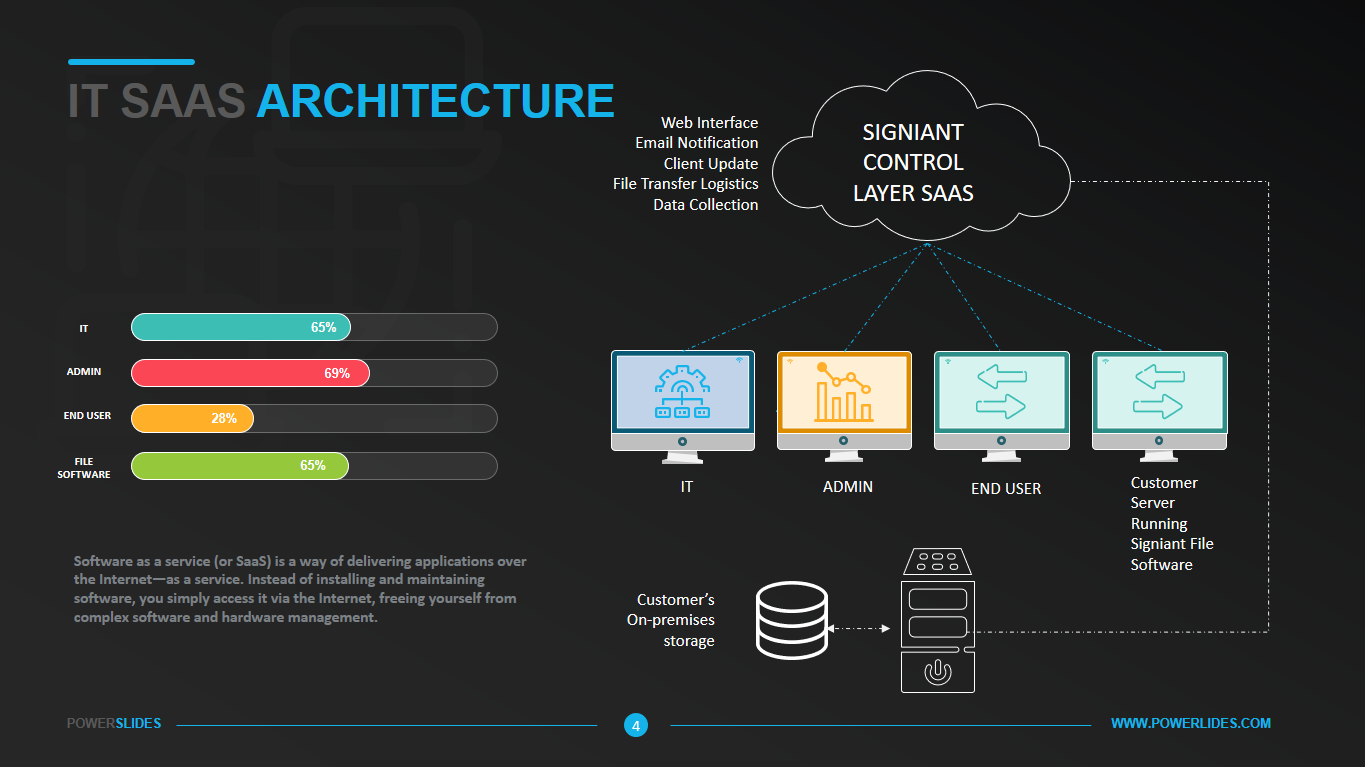
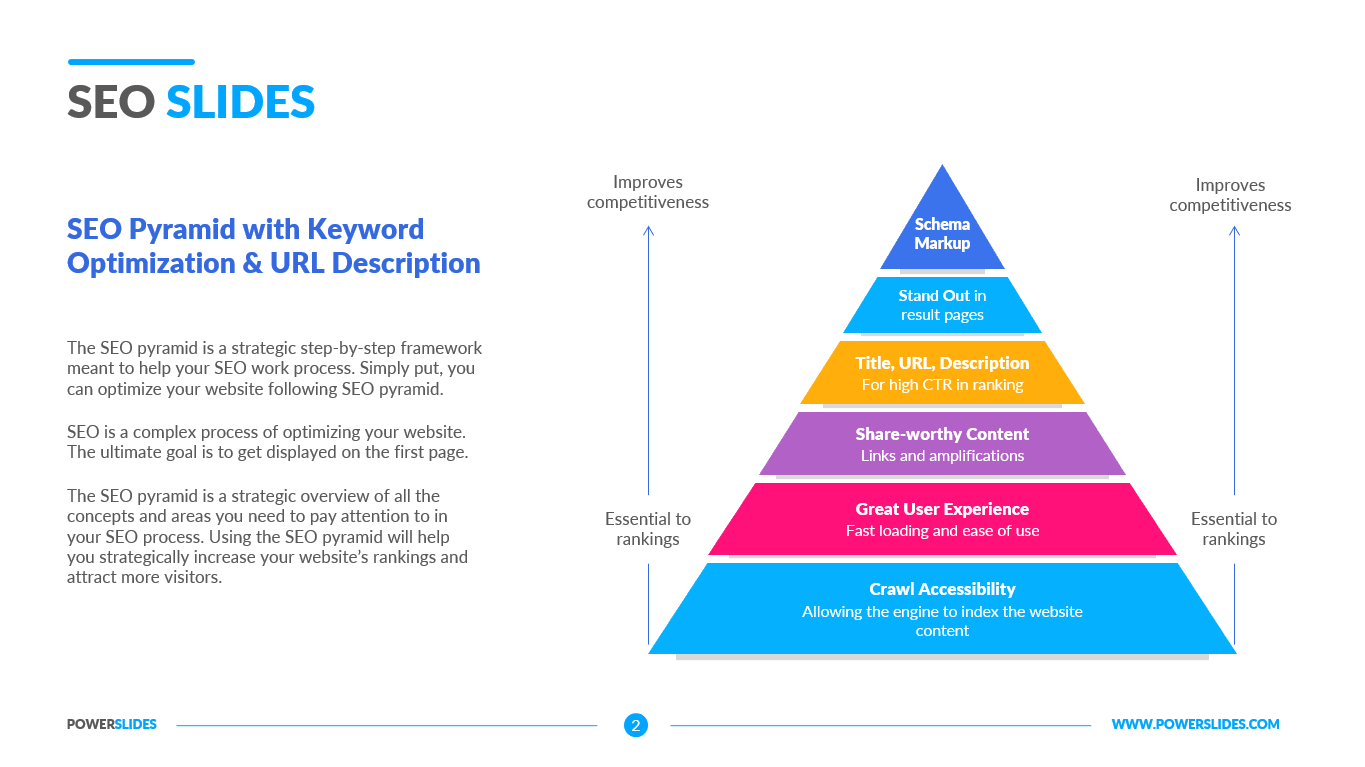
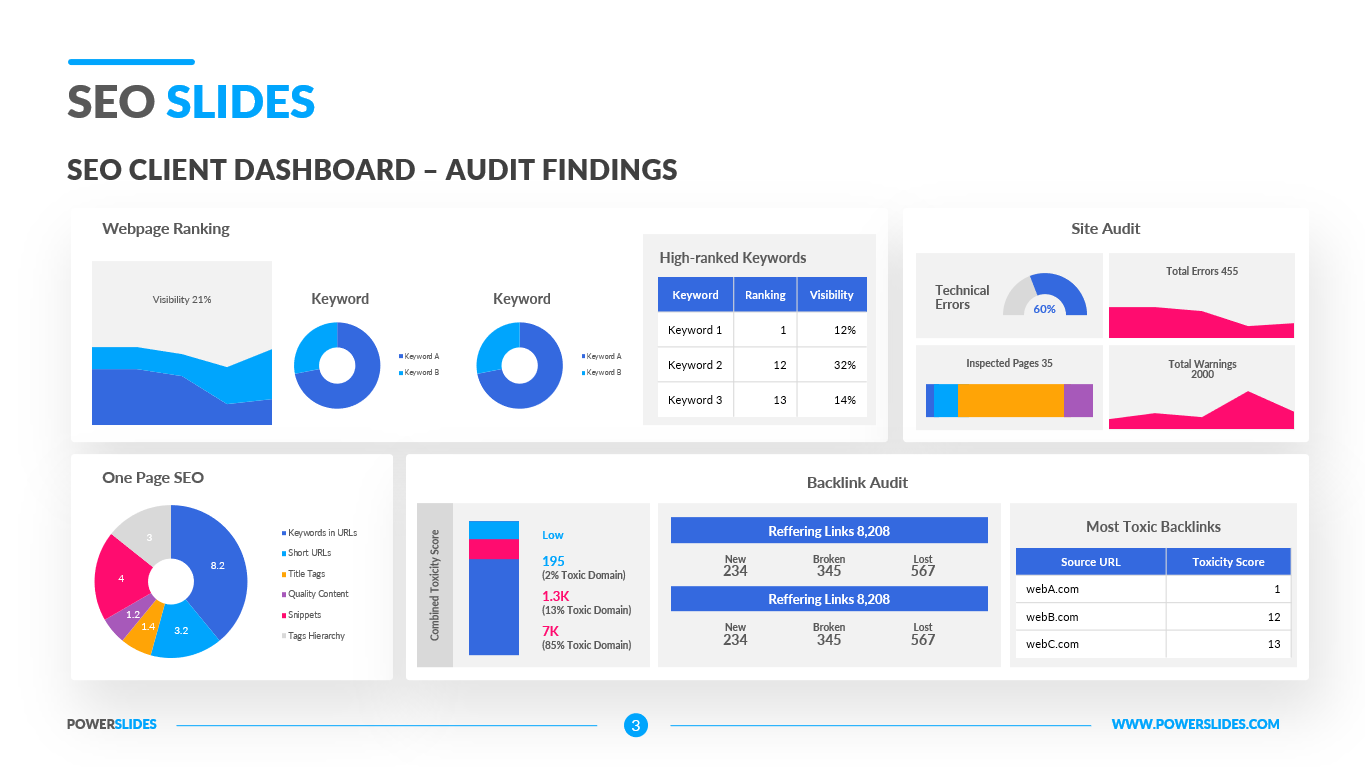
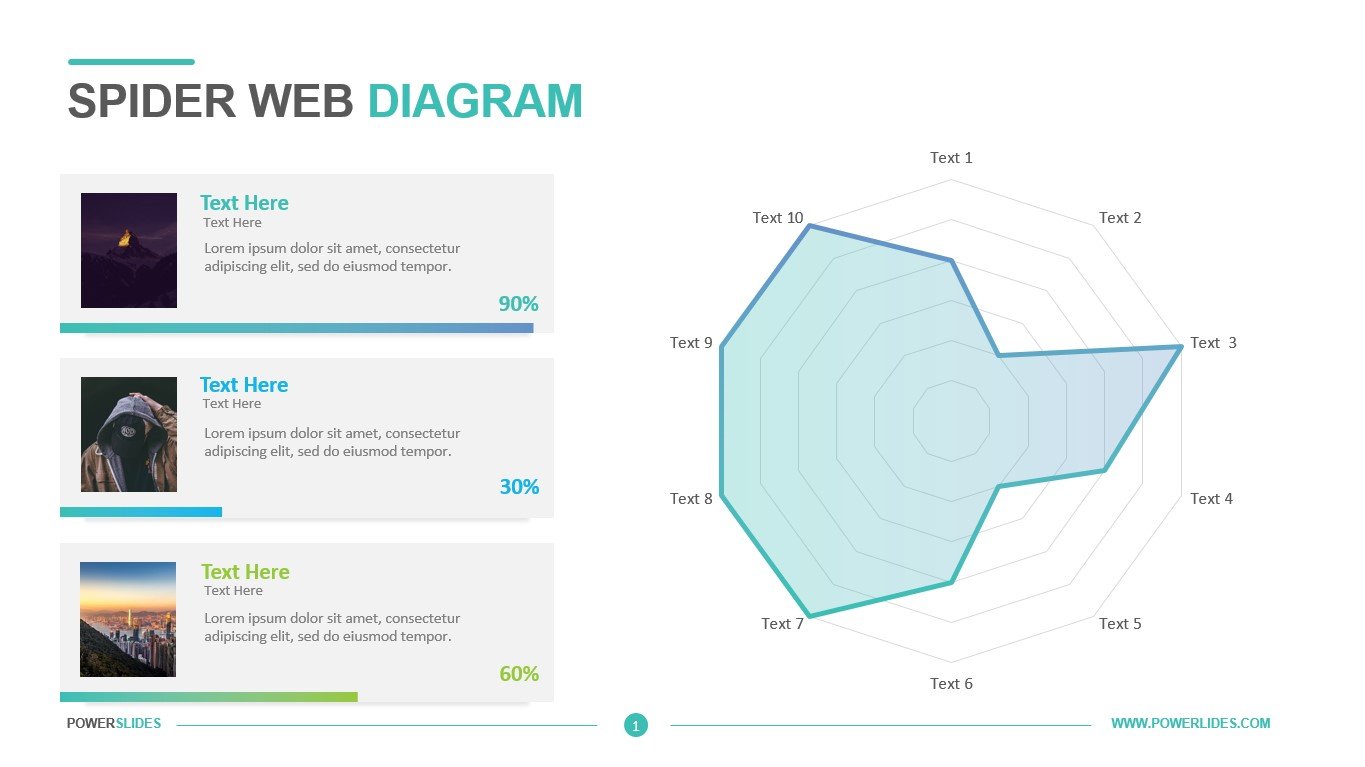
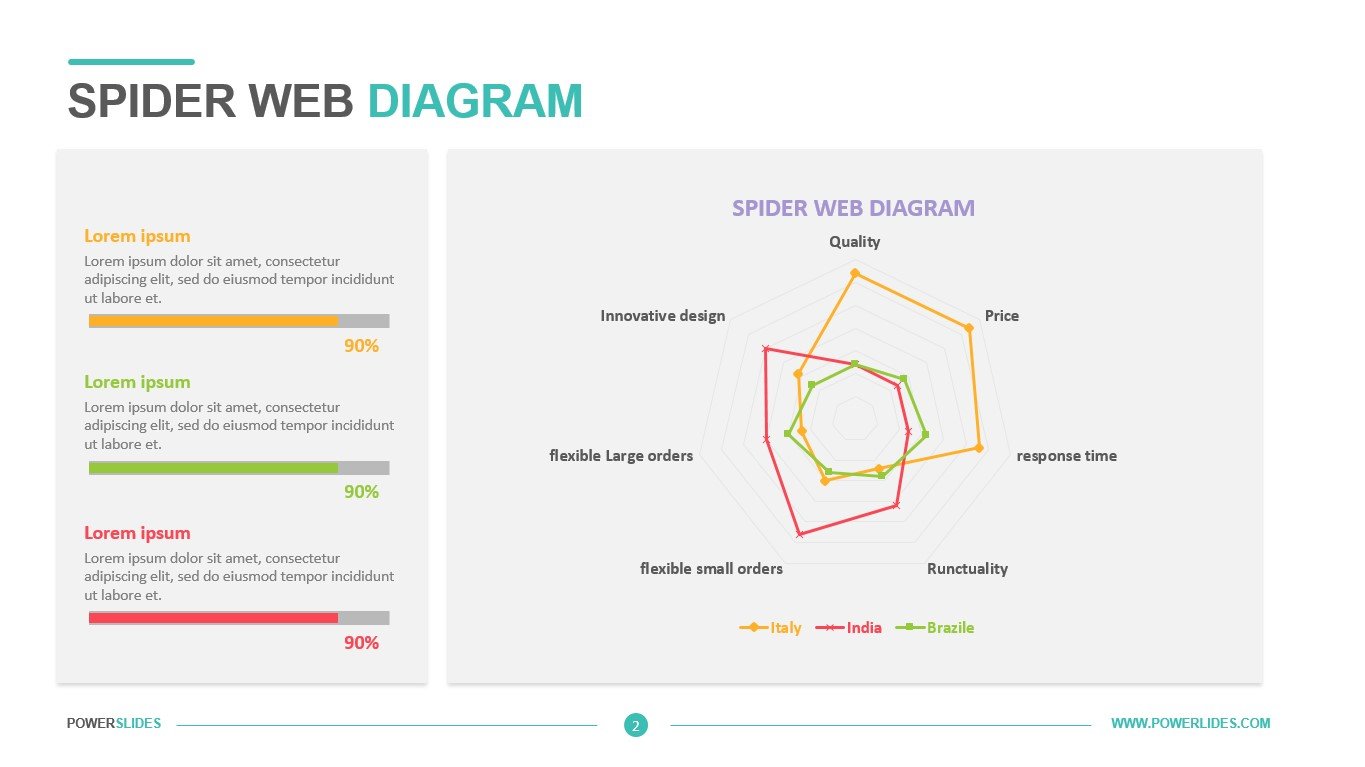
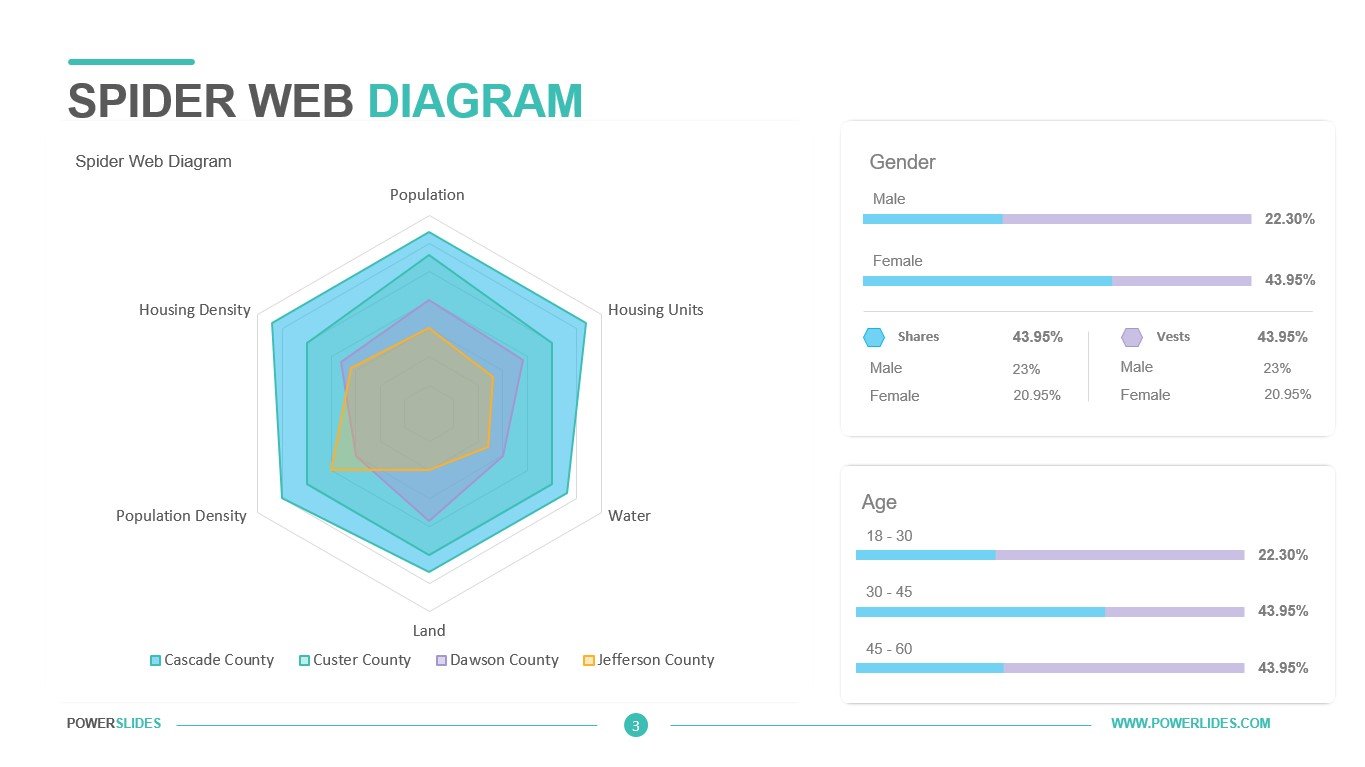
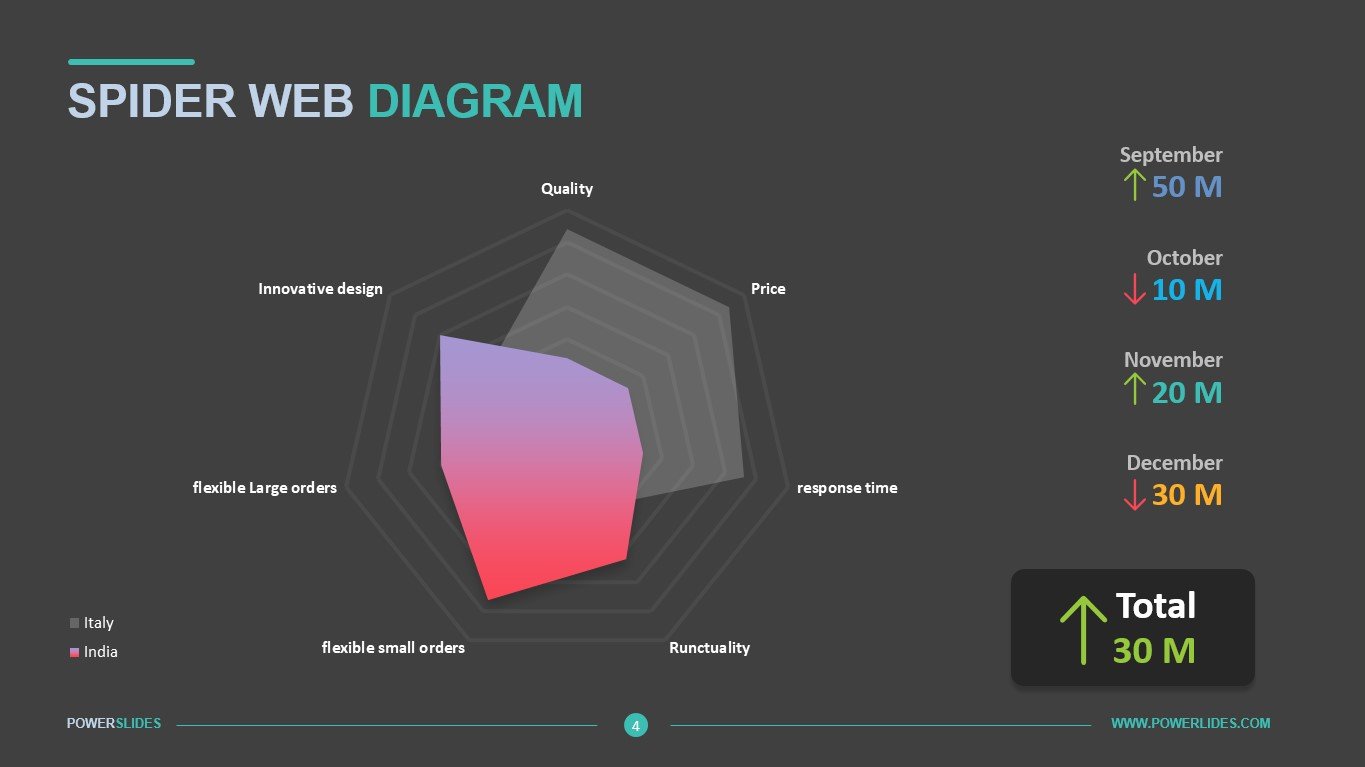
Available in four colorful and distinct designs, this template includes bar charts, flow charts, a legend for color-coded categories, and diagrams indicating hierarchy and sequences. The components include: sources, data storage, batch processing, real-time ingestion, stream processing, analysis, reporting, and orchestration. For engineers, developers and technologists who want to present their big data architecture to senior executives, this is the ideal template.
Ideal for data scientists, data analysts and technology solution architects that are designing big data infrastructures, this PowerPoint template has aesthetic appeal and simple flow charts for conveying workload processing. Big data solutions can be extremely complex, but with this 100% editable template, you can convey the concepts in a simple, straightforward manner to both technical and non-technical audiences.



 (4.80/ 5)
(4.80/ 5)